Key Benefits
The ISDA DRR significantly reduces the time, resources and cost needed to implement reporting regulations in multiple jurisdictions. Rather than interpreting and implementing each set of rules individually, and then repeating that work in future if changes are necessary, firms can implement code that has been validated and tested by industry participants and will be updated as new rules emerge or are amended, enabling resources to be reassigned to other projects.
As the DRR is based on a mutualized industry interpretation of rules in multiple jurisdictions and will be fully accessible to regulators, the potential for regulatory penalties due to incomplete or misreported data is substantially reduced.
ISDA is committed to supporting 11 core regulatory reporting regimes across nine jurisdictions: the US (under Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) rules), the EU (under the European Market Infrastructure Regulation (EMIR) and the Markets in Financial Instruments Regulation (MIFIR)), the UK (under UK EMIR and UK MIFIR), Japan, Australia, Singapore, Hong Kong, Canada and Switzerland.
The ISDA DRR is freely available to all firms.
Contact
For further information on the ISDA DRR or to get started, please contact CDMDRR@isda.org.
About the ISDA DRR
Regulators around the world are revising their reporting rules to incorporate globally agreed data standards to improve the cross-border consistency of what is reported and the format in which it is submitted. While more aligned, each set of requirements will need to be individually interpreted and implemented, with no guarantee each firm will interpret rule requirements in the same way, leading to inconsistencies and the potential for regulatory fines for those firms that get it wrong.
ISDA’s DRR addresses this by establishing a golden-source interpretation of each rule set, reviewed and agreed by an industry committee. The CDM – an open-source data standard for financial products, trades and lifecycle events – is used to convert this mutualized interpretation into open-access, machine-executable code.
Firms can implement the ISDA DRR directly as their main regulatory reporting solution, producing outgoing message reports in the required ISO 20022 format, or use it as a control function to validate their existing reporting logic. Vendors can also implement the ISDA DRR as part of their reporting solution and make it available to their customers.
Institutions involved in the development of the ISDA DRR include (but are not limited to):





JPMorganChase implements DRR using the CDM – one firm’s journey: ISDA Webinar
JPMorganChase discusses its approach and considerations in implementing ISDA DRR as a primary reporting mechanism using the open-source CDM
Features
- Reduces the costs and resource requirements that would arise from having to interpret and implement each set of rules individually.
- Cuts the risks of regulatory penalties for incorrect or misreported data.
- Delivers more accurate and consistent data to regulators, helping them to identify possible sources of systemic risk.
- Increases interoperability between firms’ reporting processes.
- Reduces reconciliation breaks in dual-sided reporting regimes.
- Enables future reporting rule revisions to be easily delivered via centralized DRR reporting code changes.
- Reports generated in DTCC’s Harmonized XML for Canada or the ISO 20022 format for other reporting jurisdictions, which can be submitted directly to trade repositories.
Resources
- Module A: Introduction to the CDM
- Module B: Accessing the CDM
- Module C: How the CDM works
- Module D: How the CDM is used
- Module F: Advanced Features
- Module G: Getting Started with CDM for DRR
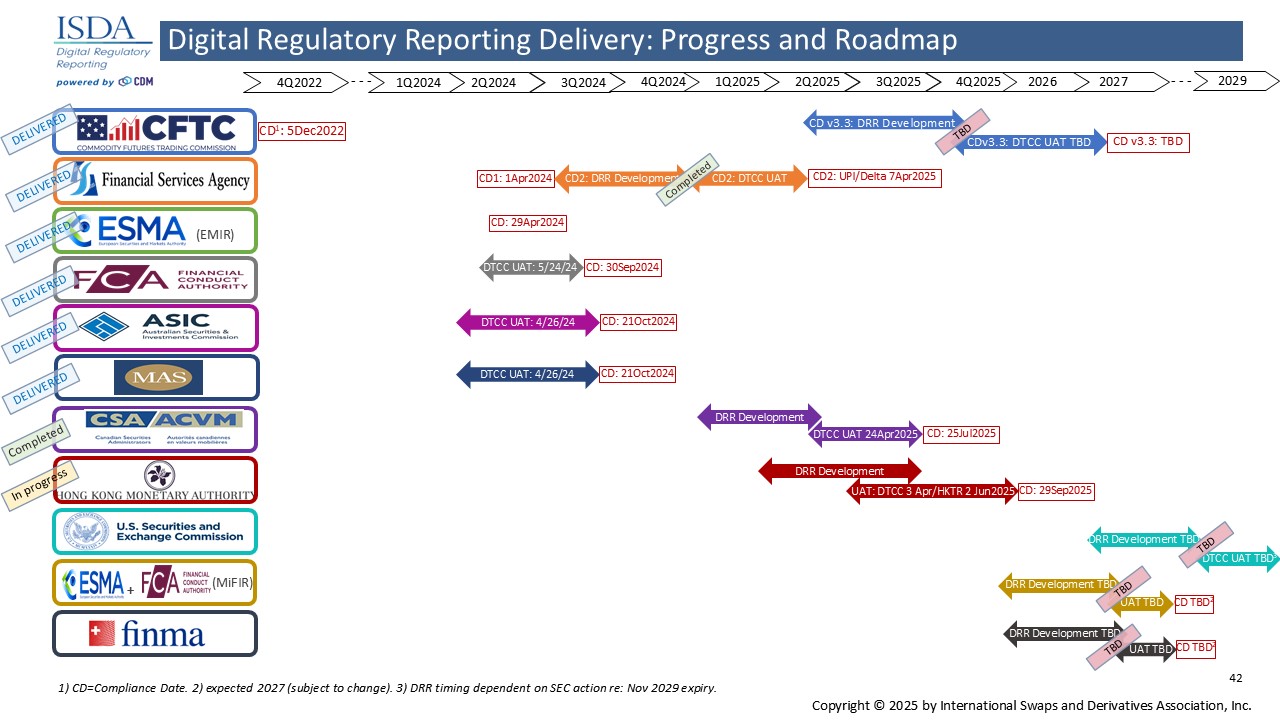
Coverage
The ISDA DRR will cover regulatory reporting rules in all major jurisdictions and ISDA is committed to supporting the DRR in future by incorporating all future amendments.
- The first iteration of the DRR was launched ahead of the initial set of reporting rule changes introduced by the US Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) on December 5, 2022.
- The ISDA DRR has since been extended to cover amended rules in Japan (April 1, 2024), EU for reporting rules under EMIR (April 29, 2024), UK EMIR (September 30, 2024), Singapore (October 21, 2024), Australia (October 21, 2024) and Canada (July 25, 2025).
- The ISDA DRR is currently in the process of being further extended to cover rule amendments for Hong Kong (September 29, 2025).
- All further updates, including amendments to CFTC and MiFIR in the EU and UK, will be incorporated into the ISDA DRR well in advance of compliance dates.
Fact Sheets/Presentations
- May 2025: Digital Regulatory Reporting Fact Sheet
- April 17, 2024: ISDA AGM 2024: Eric Litvack Chairman Remarks
- April 16, 2024: ISDA AGM 2024: Day 1 Scott O’Malia Opening Remarks
- February 28, 2024: CDM Showcase 2024: Scott O’Malia Afternoon Remarks
- March 28, 2022: Digital Regulatory Reporting: Market and Regulatory Initiatives
- ISDA DRR Working Groups – Terms of Reference
Press Releases/Blogs
- May 13, 2025: DRR Extended to Support Revised Canadian Rules
- May 7, 2025: ISDA to Extend DRR to cover MIFID/MIFIR Reporting
- January 15, 2025: JSCC to adopt Digital Regulatory Reporting (DRR)
- October 30, 2024: JPMorgan implements open source solution to transform regulatory reporting
- July 8, 2024: ISDA’s Commitment on Data Reporting
- April 17, 2024: ISDA Extends Digital Regulatory Reporting Initiative to New Jurisdictions
- February 26, 2024: DRR: The Answer to Reporting Rule Rush
- November 16, 2023: The Swap Podcast: Reporting Revamp
- October 17, 2023: Hidden in Plain Sight?
- February 27, 2023: Continuing Our Digital Journey
- November 28, 2022: A Digital Approach to Reporting
- November 22, 2022: ISDA Launches Digital Regulatory Reporting 1.0 and Opens Access to Entire Market
- November 2, 2022: ISDA and BNP Paribas Successfully Test Digital Regulatory Reporting for CFTC Rules
- September 30, 2022: Efficiency Through Reporting Best Practice
- February 3, 2022: All About Transparency
- November 15, 2021: The Efficient and Scalable Answer to CFTC Reporting Compliance
- February 17, 2021: Time to Digitize Trade Reporting
- October 6, 2020: ISDA and REGnosys Win G-20 TechSprint For Regulatory Reporting
- August 6, 2020: Digital Benefits: A Member Perspective
- July 30, 2020: A Digital Call to Arms
- July 27, 2020: ISDA and ISLA Agree to Closer Collaboration on Digital Initiatives
- May 21, 2019: ISDA CDM Deployed to Help Deliver UK Digital Regulatory Reporting Pilot
Webinars/Videos
- May 21, 2025: ISDA AGM Studio: Pictet and and JPM Chase overview reasons they implemented DRR/CDM
- March 20, 2024: ISDA DRR/CDM Training Sessions Webinar
- January 2024: ASIC and MAS Digital Regulatory Reporting DRR Kick-Off Webinar 2024
- May 12, 2022: Introduction to ISDA’s Digital Regulatory Reporting Initiative
- How Are Trade Reporting Rules Developed for DRR?
- Demo of the ISDA DRR


